World Hepatitis Day, 28th July
World Hepatitis Day is a global public health campaign marked by the World Health Organization and observed on July 28 every year. Its aim is to encourage better awareness, prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of an illness that kills close to 1.35 million people each year; affects hundreds of millions of people worldwide; and can lead to other serious and fatal liver diseases.
What is hepatitis?
Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. It comes from the Greek words “hepar” meaning liver, and “-itis” meaning inflammation. Inflammation or swelling, generally occurs in organs of the body when they are damaged by injury or infection.
The liver is one of the largest and most essential organs in the human body, supporting almost every other organ. It has around 500 different responsibilities. It processes and manages blood, controlling clotting, filtering waste products, and regulating chemicals carried in the bloodstream, such as cholesterol and glucose. It also creates bile which helps break down food and aids digestion, along with many more functions.
The most common cause of hepatitis is a viral infection, hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E. Other types of hepatitis can be caused by heavy or overuse of alcohol and drugs, infections, toxins, complications from other illnesses and autoimmune disease.
Hepatitis can be a temporary condition (acute), or long term (chronic). Hepatitis itself can be a serious disease, but it also leads to other life-threatening illnesses such as liver cancer, cirrhosis, and liver failure.
Viral hepatitis
Viral infections are the most common causes of hepatitis, types A, B, C, D, and E. The main differences between the strains being how transmission occurs, the severity of the illness, and prevention and treatment methods. Hepatitis A, B, and D are preventable with immunisation. There is currently no vaccine for types C or E.
With types A and E, the virus is generally spread through contact with contaminated water or food. Hepatitis B is most often sexually transmitted or caught through infected blood. Hepatitis C is contracted through infected blood. Type D can only be caught by people already infected with B.
The symptoms of hepatitis vary from person to person and can depend on the type of hepatitis the person has. A and E are often acute, and the signs appear quickly. B and C are more likely to go undetected and not be picked up until they have already caused damage which affects the function of the liver, causing a chronic long-term illness.
Types B and C are the most common cause of liver cirrhosis, cancer, and viral hepatitis-related deaths. There are antiviral medications available to treat chronic viral hepatitis B and C. It is estimated that there are 325 million people living with these diseases globally.

Alcoholic hepatitis
The excessive consumption of alcohol can lead to alcoholic hepatitis and other liver diseases, such as fatty liver and cirrhosis. One of the liver’s functions is to break down toxins, such as alcohol and drugs. If you are consuming more alcohol than the liver can process, whether that is the amount or frequency of which you drink, then the organ can become seriously damaged.
There are conflicting opinions on whether alcoholic hepatitis is completely curable. Any treatment program will include complete abstinence from alcohol, and would aim to reduce or eliminate symptoms, with the hope that any damage can be halted if not wholly reversed. Some regeneration of the liver is possible, though scarring tends to be permanent.
You can reduce your risk of developing alcoholic hepatitis by controlling how much you drink.

Signs and symptoms of hepatitis
The symptoms of acute hepatitis appear quickly and can include:
- Weight loss
- Loss of appetite
- Tiredness and exhaustion
- Flu-like symptoms
- Pain in the abdominal area
- Dark urine and pale stool
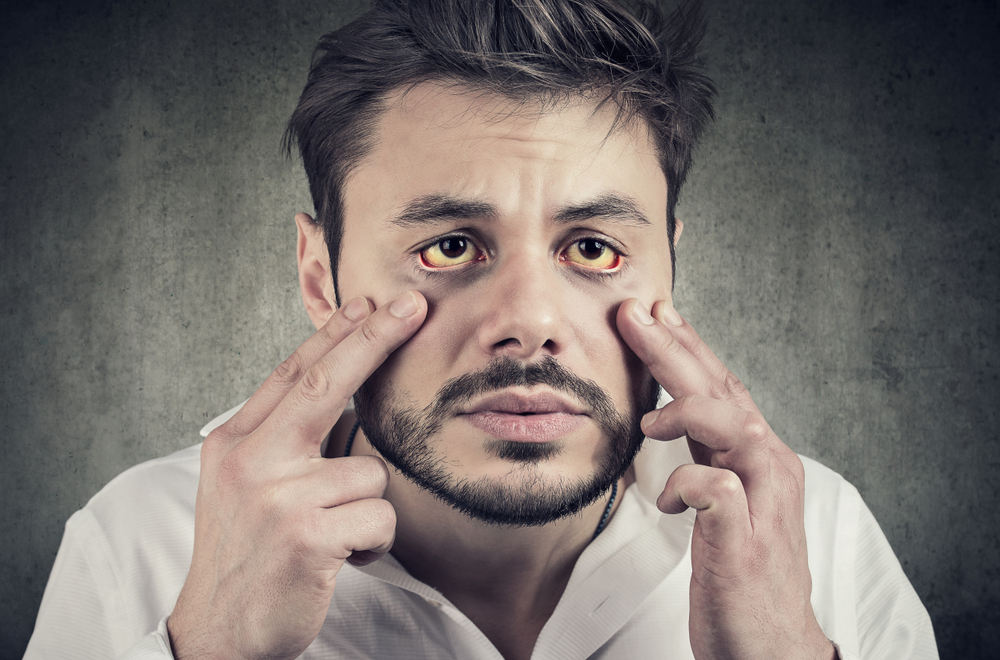
- Jaundice – characterised by yellow skin and eyes
With chronic hepatitis, the signs are often slower to develop and may be too subtle to notice until the liver stops functioning properly. Symptoms include:
- Jaundice
- Swelling in the legs, ankles, and feet
- Confusion
- Blood in stools or vomit
The risks of hepatitis B and C to drug addicts
Alongside alcoholic hepatitis, the viruses B and C are the most dangerous for alcoholics and addicts. Both are bloodborne pathogens that are transmitted by the direct transfer of infected blood. Hepatitis C is one of the most widely spread blood-borne viruses.
Hepatitis B is highly contagious and is contractable through contact with any infectious body fluids, blood, semen, and vaginal secretions, making it a serious sexually transmitted disease. Hepatitis C, whilst not as common, can also be transferred during sexual contact.
The potential of sharing an infected needle during intravenous drug use puts addicts in a high-risk category. Engaging in risky sexual behaviour or with multiple sex partners, whilst heavily intoxicated or under the influence of alcohol and drugs, put alcoholics and addicts at risk of catching these and other STDs.

Rehab in Spain
Located on the idyllic island of Ibiza we are the most personalised addiction and rehab treatment clinic in Spain and Europe. We use a combination of one-to-one and group counselling, transcranial magnetic stimulation, cognitive behavioural and equine facilitated therapy.
We have a highly experienced team of fully qualified staff available to treat our clients for problems with drugs, alcohol, addiction and related mental health conditions. For information on admission to our luxury rehab centre please contact [email protected]
Share this information, choose your platform!
Gambling Addiction
Gambling can be a fun and exciting recreational activity; the nervous anticipation of the next card to be dealt, or rolling the dice, perhaps the heightened enjoyment of a football match on which you have a small monetary stake? What’s …
Mood disorders: depression and bipolar
Everyone feels a little low at times; maybe we don’t feel like socialising, find it difficult to get motivated, and just want to stay at home and duvet dive. Particularly if we’ve experienced an emotional or physical upset; and especially …
The dangers of buying drugs online
Anyone that has access to the internet will have been subjected to pop-ups with offers of cheap medication delivered to your door, or maybe it is your email account that has been bombarded with spam ads claiming they can sell …
Dopesick – Opioids and Addiction
In the hard-hitting Disney+ drama “Dopesick”, despite there being several fictional characters, the narrative is centred on real-life people and a true story. The series is based on the 2018 non-fiction book by Beth Macy, “Dopesick: Dealers, Doctors and the …









